Click the button to start reading
Tuning Up Business Performance with Process Improvement Methodologies: Six Sigma, Lean, and Kaizen
Ever had that sinking feeling that your business is stuck in the mud, spinning its wheels instead of speeding towards success?
It’s a familiar scenario for many, but there’s a powerful solution at hand – process improvement methodologies.
These strategic approaches are not just the flavor of the month. They’ve become game-changers in our fast-evolving business ecosystem, playing a crucial role in helping companies optimize their processes, enhance productivity, and boost their bottom line.
From Six Sigma to Kaizen, the different approaches available for process improvement means there’s a solution out there for every type of business and team.
In this article, we’re embarking on a journey to explore the fascinating world of process improvement methodologies. We’ll delve into why they are more important than ever for businesses today, and how they can revolutionize your operational efficiency.
What Are Process Improvement Methodologies in Business?
Process improvement methodologies are systematic approaches designed to facilitate the analysis, redesign, and implementation of better processes within an organization. These methodologies, often formulated based on various principles and theories, provide a structured way to identify issues, find solutions, and realize improvements.
Examples of such methodologies include Six Sigma, Lean, Kaizen, Business Process Modeling, and Total Quality Management (TQM), each with its unique approach and focus.
Whether the goal is to enhance quality, reduce waste, boost productivity, improve customer satisfaction, or achieve other operational efficiencies, these methodologies provide the tools, techniques, and frameworks necessary for businesses to systematically improve their processes.
Due to the dog eat dog world of business, mere survival requires organizations to constantly innovate and improve. This is where process improvement methodologies come into play. They help businesses identify their inefficiencies, understand the root causes, and implement effective solutions. Here’s some of the ways process improvement methodologies and tools can help:
- Identify Inefficiencies: Process improvement methodologies help businesses pinpoint their inefficiencies, making it possible to understand where changes need to be made.
- Root Cause Analysis: These methodologies facilitate understanding of the root causes behind process issues, not just the symptoms. This deeper analysis can lead to more effective, long-lasting solutions.
- Effective Solutions: Once problems are identified and understood, process improvement methodologies guide businesses in implementing effective solutions that lead to significant enhancements in operational efficiency.
- Eliminate Redundancy: They aid in identifying and eliminating redundant tasks, thereby saving time and resources.
- Streamline Workflows: These methodologies help in streamlining workflows, ensuring smoother, faster, and more efficient processes.
- Reduce Errors: By focusing on quality, process improvement methodologies can drastically reduce error rates, leading to higher quality outputs and less time spent on rework.
- Improve Service Delivery: They can enhance service delivery times, leading to better customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: Improvements in operational efficiency often translate into cost savings, a crucial factor in enhancing profitability.
- Customer Satisfaction: Higher operational efficiency and improved service delivery can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Most importantly, perhaps, these methodologies often foster a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. This mindset, when ingrained into the fabric of the organization, can result in sustained performance enhancement, agility in the face of change, and a solid foundation for long-term success.

Six Sigma: A Data-Driven Approach
When it comes to business process improvement methodologies, Six Sigma often steals the limelight.
Originating in the manufacturing sector at Motorola, Six Sigma has now permeated various industries, showcasing its universal applicability and effectiveness.
Here’s the make up of Six Sigma’s data-driven approach:
- Define the problem or improvement area.
- Measure the current process and collect relevant data.
- Analyze the data to identify root causes of defects.
- Improve the process by implementing and verifying the solution.
- Control the future state of the process to prevent reverting to the old method.
It’s especially beneficial in environments where reducing variability and eliminating defects can lead to significant cost savings and quality improvements, such as healthcare, finance, supply chain, and IT.
Advantages of Six Sigma:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Six Sigma uses statistical methods to improve processes, making decisions more objective and reducing the influence of biases.
- Reduction in Variability: Six Sigma aims at reducing variability in process outputs, which enhances product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: By reducing defects, Six Sigma can save organizations significant costs associated with rework, product returns, and lost customers.
- Structured Methodology: The DMAIC framework provides a structured approach to problem-solving, ensuring consistency and effectiveness.
Disadvantages of Six Sigma:
- Resource Intensive: Implementing Six Sigma requires significant resources, both in terms of time and personnel training.
- Limited Creativity: The focus on reducing variability may limit creativity and innovation, potentially hindering the development of new ideas.
- Requires Expertise: Effective use of Six Sigma requires trained professionals, which could increase the costs for a business.
The proof is in the pudding, and General Electric’s experience with Six Sigma shows it. The company invested heavily in Six Sigma and reaped an estimated $12 billion in savings over five years.
When thinking about process improvement models and methodologies, Six Sigma holds its own.
Its emphasis on statistical rigor sets it apart and makes it a solid contender among a list of process improvement methodologies.
As a continuous process improvement methodology, it’s designed to constantly seek perfection. In the hands of the right team, Six Sigma can become a powerful weapon for organizational excellence.
Lean: Maximizing Value, Minimizing Waste
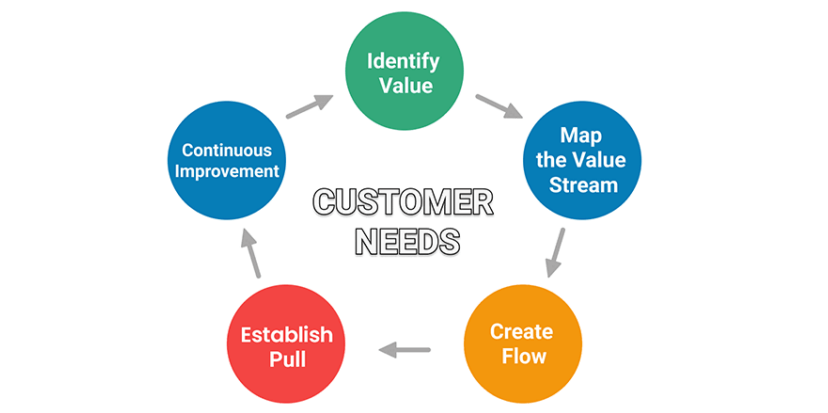
The Lean methodology, inspired by the manufacturing practices at Toyota, is a paradigm shift that seeks to maximize value for the customer while minimizing waste. This process improvement methodology fundamentally changes the way we view and manage operations, focusing on eliminating any process that does not add value.
Lean methodology, at its core, is about creating more value with fewer resources. It identifies and eliminates ‘waste,’ anything that doesn’t contribute to the end product or service’s value. Lean focuses on the value stream, ensuring each step contributes towards the ultimate goal: delivering a product or service that meets customer needs with minimal resources.
However, as enticing as the Lean approach sounds, it does have its fair share of strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages of Lean:
- Elimination of Waste: Lean focuses on identifying and eliminating waste in all forms, improving overall efficiency.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: By focusing on value from the customer’s perspective, Lean can lead to enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Lean streamlines processes and improves workflow, increasing operational efficiency and productivity.
- Adaptable Across Industries: The principles of Lean can be applied across various sectors, making it a versatile methodology.
Disadvantages of Lean:
- Requires Cultural Change: Similar to Kaizen, Lean requires a significant cultural shift within the organization, which can be challenging to achieve.
- Short-Term Focus: Lean may lead to an overemphasis on short-term productivity gains at the expense of long-term strategy.
- Risk of Over-Optimization: While focusing on efficiency, companies may risk over-optimization, leaving little room for flexibility or unexpected changes.
Lean’s intense focus on cost-cutting and efficiency can sometimes lead to a myopic view, neglecting other essential aspects like employee wellbeing and customer relationships.
Despite these challenges, Lean has successfully been implemented across various industries. One notable example is the Boeing 737 factory in Renton, Washington. The factory adopted Lean manufacturing principles which lead to a more productive workspace ultimately leading to triple the monthly output at the plant.
The Lean methodology’s philosophy of maximizing value and minimizing waste makes it a powerful tool for businesses across a wide array of industries. However, it requires a shift in organizational culture and commitment from all levels of the organization. With the right implementation, the rewards can be significant, leading to improved efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability.
Kaizen: The Philosophy of Continuous Improvement
Originating from Japan, Kaizen stands for “continuous improvement.” It’s not just a methodology; it’s a culture, a way of thinking that permeates every level of an organization. Kaizen works under the philosophy that small, incremental improvements can lead to significant positive changes over time.
It encourages everyone in the organization, from the CEO to the front-line workers, to participate in improving processes, eliminating waste, and boosting efficiency and productivity.
Advantages of Kaizen:
- Incremental Improvements: Small, continuous changes are easier to implement and are often met with less resistance from employees compared to larger, drastic changes.
- Employee Engagement: Kaizen involves all employees in the improvement process, which can boost morale, increase job satisfaction, and lead to a more engaged and productive workforce.
- Reduction of Waste: With its focus on continual improvement, Kaizen encourages the identification and elimination of waste in all forms, improving efficiency and productivity over time.
- Promotes a Learning Culture: Kaizen encourages an environment of constant learning and adaptation, keeping companies agile and competitive.
Disadvantages of Kaizen:
- Requires Cultural Shift: Implementing Kaizen can be a significant challenge as it requires a deep-seated cultural change within an organization. This can be difficult to achieve, especially in hierarchical organizations where decision-making is typically top-down.
- Time-Intensive: The focus on small, continuous changes means that substantial improvements can take time to become evident.
- Not Suited for Immediate, Drastic Changes: When immediate, significant changes are required, the incremental approach of Kaizen may not be the best fit.
Kaizen has been successfully adopted by numerous organizations around the world. Toyota is perhaps the most famous example of Kaizen in action. Through continuous incremental improvements, Toyota has become a global leader in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Kaizen is a potent methodology for companies that are willing to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. It’s about creating an environment where every employee feels empowered to suggest and implement improvements, no matter how small. It’s a journey rather than a destination, a way of thinking that can transform a business and lead to lasting success.

Business Process Modeling (BPM): Visualizing Improvement
Business Process Modeling, or BPM for short, is a method that involves creating a visual representation of a company’s processes. This graphical model can serve as a blueprint, detailing the sequenzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzzce of activities, the parties involved, the decision points, and the information flows.
Essentially, BPM allows a business to see the complete picture of how individual processes interact, enabling a better understanding of the entire system. It’s like having a map that guides you through the complexities of your business landscape.
Advantages of BPM:
- Transparency and Visibility: BPM offers an at-a-glance view of an organization’s processes. This transparency can help identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
- Improved Collaboration: By providing a clear, visual representation of processes, BPM facilitates better communication and collaboration among teams.
- Risk Mitigation: BPM allows for the early identification of potential risks and challenges, leading to proactive mitigation and reduction in costly mistakes.
Disadvantages of BPM:
- Time-Consuming: The process of mapping out all the business processes can be quite time-consuming, especially in complex organizations.
- Requires Maintenance: As processes change and evolve, so too must the BPM. This constant updating can be resource-intensive.
- Limited Flexibility: BPM models can sometimes become too rigid, preventing quick adaptation to changes in the business environment.
BPM has found success across a variety of industries and scenarios.
In healthcare, it’s used to map out patient care processes, from admission to discharge, ensuring optimal patient experiences. In manufacturing, BPM aids in visualizing production workflows, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
Over in software development, BPM helps in outlining the process from concept to code, enhancing understanding and cooperation among development teams. In all these cases, BPM serves as a tool for understanding, communicating, and improving business processes.
Total Quality Management (TQM): Pursuing Excellence
Total Quality Management, or TQM, is a comprehensive and structured approach to organizational management that seeks to improve the quality of products and services through ongoing refinements in response to continuous feedback.
TQM requires the involvement of all employees, from top management to the shop floor, in a collaborative effort to improve performance at every level. At the center, TQM revolves around three primary principles – customer satisfaction, employee involvement, and continuous improvement in quality.
Advantages of TQM:
- Improved Quality: As the name suggests, TQM’s primary goal is to improve the quality of products or services. This can lead to better customer satisfaction and increased market share.
- Increased Employee Morale: TQM encourages the participation of all employees, which can lead to improved morale, motivation, and job satisfaction.
- Long-Term Success: By focusing on continuous improvement, TQM can help an organization achieve long-term success.
Disadvantages of TQM:
- Requires Cultural Change: Implementing TQM often requires a significant shift in the company’s culture, which can be challenging and time-consuming to achieve.
- Time and Cost Intensive: TQM is not a quick fix. It requires ongoing effort, resources, and commitment, which may be beyond the capacity of some businesses.
- Delayed Results: The benefits of TQM may not be immediately visible, leading to frustration and potential abandonment of the method.
Many companies across various sectors have successfully implemented TQM.
For example, Toyota is famous for its commitment to TQM and has set the standard for high quality in the automotive industry. In the service sector, Ritz-Carlton, a renowned name in luxury hospitality, has employed TQM principles to enhance guest satisfaction and set a benchmark in the industry.
What Is the Role of Tools in Process Improvement?
Process improvement tools are software applications, methodologies, and techniques that assist in implementing, monitoring, and optimizing business processes. They come in a variety of forms, including project management software, data analysis tools, process mapping software, and automation technologies.
One such tool that’s going to be a great asset to your continuous improvement journey is Teamly.
Teamly is a project management tool built specifically for the needs of modern, often remote, teams. It incorporates real-time chat for team communication, task management for tracking progress, and time tracking to ensure efficiency.
It also offers features like screen capture video and audio recording to aid in communication and accountability. Teamly is designed to handle both the big picture and the fine details, making it a comprehensive solution for managing and improving business processes.
Choosing the right tools for process improvement is pivotal for a number of reasons.
- Efficiency: Tools that can automate routine tasks, free up time for employees to focus on more strategic, high-value tasks.
- Collaboration: Tools like Teamly that enable real-time communication and collaboration can break down silos, promote transparency, and encourage team members to work together towards common goals.
- Tracking and Monitoring: With the right tools, you can track and monitor processes in real-time, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and implement timely improvements.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Many process improvement tools offer analytics and reporting features, providing valuable insights that drive informed, data-driven decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: By providing visibility into processes and performance, these tools can support a culture of continuous improvement, enabling teams to regularly evaluate and enhance their processes.
Tools are not just facilitators—they can be game-changers. Whether it’s a comprehensive solution like Teamly or a combination of specialized tools, finding the right fit can be a significant step towards business efficiency and success.
Conclusion
Each methodology, be it Six Sigma’s data-driven approach, Lean’s focus on reducing waste, or Kaizen’s continuous improvement has its own merits and suitability.
However, what remains common across all methodologies is their goal: to enhance operational efficiency, reduce waste, and drive customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to improved business performance and growth. Irrespective of the methodology chosen, the underlying principle should always be to encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
Embrace change.
Those willing to continuously analyze, adapt, and improve their processes will be the ones to stand tall. Remember, perfection is not a destination, it’s a journey. Equip yourself with the right knowledge, tools like Teamly, and an unyielding commitment to improvement, and you’ll set your business on the path to sustainable success.