Click the button to start reading
PERT in Project Management: What It Is and How to Use It (With Examples)
Aren’t project managers a curious bunch? They’ve got this itch for innovation and excellence. They constantly seek that one thing that could turn their projects into absolute marvels. Well, that’s where PERT in project management comes into play.
Whether you’re creating the next big app, putting together an art show, or even launching a fashion line, PERT is your trusty friend.
In this blog post, we’ll reveal how PERT in project management works and the steps to use it effectively. Plus, we’ll look into the main components of PERT and its limitations.
But there’s more.
As we move on, you’ll get examples and discover when PERT charts are most effective.
What Is PERT in Project Management?
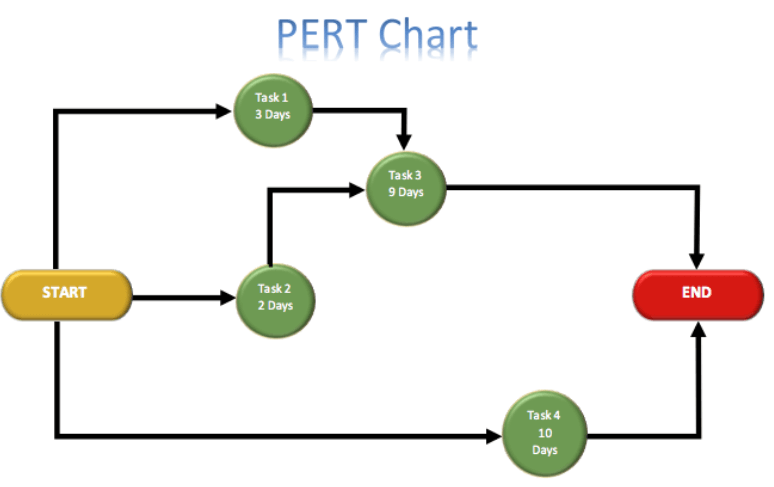
Image source: Quora
PERT is a way of managing complicated projects that are full of uncertainties. The acronym stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique. This project management technique helps in planning, scheduling, and organizing projects that are hard to predict.
In simple words, PERT gives us a map of what to do and when, helping us to single out the most important tasks.
How Does PERT Work?
Being one of the project management techniques, PERT uses a special diagram to show the order of tasks in a project.
This diagram has boxes (for tasks) and lines (for connections between tasks).
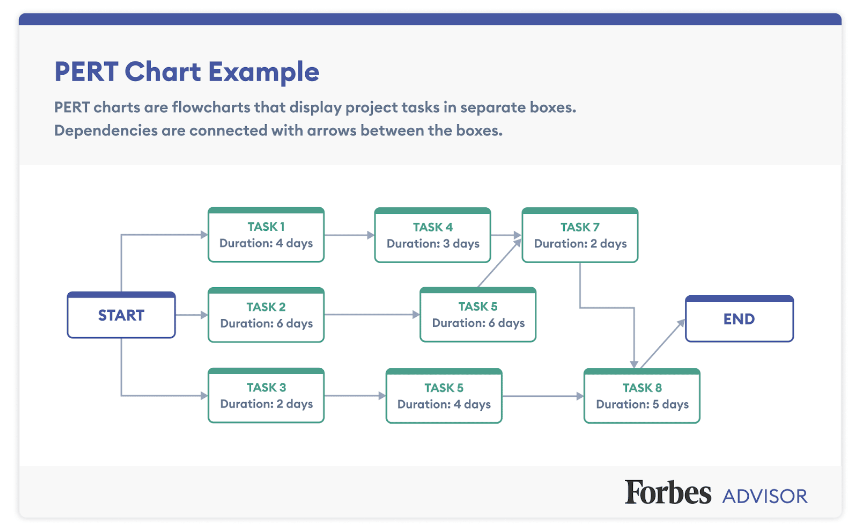
Image source: Forbes
For each task, we guess how long it might take. But since we can’t be sure, we make three guesses: the quickest time, the most likely time, and the longest time. Then, we use these guesses to figure out the average time the task will probably take.
Some tasks are really important and need to be done exactly on time, or the whole project will be delayed. PERT helps us find these crucial tasks. And we call this important sequence of tasks the “critical path.”
Other tasks can be delayed a bit without causing problems. PERT shows us how much they can be delayed without messing up the project.
When we add up all the average times for the tasks on the critical path, we get an idea of how long the whole project might take.
Also, PERT helps us guess the chance of finishing the project by a certain time. This is useful for planning and making decisions about when to use resources.
How to Calculate Activity Durations Using PERT?
Calculating the expected time for each activity in PERT involves a formula that takes into account the optimistic time (O), the most likely time (M), and the pessimistic time (P) estimates for the activity.
Here’s the formula and the steps to calculate the expected time:
Formula: Expected Time (TE) = (O + 4M + P) / 6
Steps to Calculating Expected Time with PERT
Step 1: Gather Estimates: Get three time estimates for the activity:
- Optimistic Time (O): The shortest time the activity could take if everything goes exceptionally well.
- Most Likely Time (M): The time the activity would take on average, considering normal conditions.
- Pessimistic Time (P): The longest time the activity might take, accounting for possible delays or challenges.
Step 2: Plug into the Formula: Substitute the values of O, M, and P into the formula for expected time (TE).
Step 3: Calculate: Add up the values of O, 4M, and P, and then divide the sum by 6. This gives you the expected time for the activity.
For example, if O is 3 days, M is 6 days, and P is 10 days:
Expected Time (TE) = (3 + 4 * 6 + 10) / 6
Expected Time (TE) = 6.17 days (approximately)
This expected time gives you a more balanced estimate that considers all the possible scenarios for completing the activity.
Limitations of PERT in Project Management
While PERT diagrams are powerful tools, they’re not magical. Like any tool, they work best when used thoughtfully and in the right situations. Remember, it’s not just about drawing lines; it’s about understanding your project’s landscape.
Keeping Realistic Expectations
Just as a car can’t fly, PERT diagrams have their limits. They work well when tasks are well-defined, but they struggle with highly uncertain tasks.
Reliance on Guesswork
Unfortunately, estimating task times isn’t always accurate. PERT diagrams rely on these estimates, so be aware that they’re educated guesses, not certainties.
Struggles with Complexity
Creating PERT diagrams for small projects is easy. However, for big, intricate projects, you have to deal with many parts and aspects. Well, it can get complicated.
The Human Factor
PERT diagrams rely on your guesses and judgment. If these aren’t accurate, the whole plan might not work as expected. It’s like making a map with not-so-clear directions.
Project Changes
Imagine you’re building a sandcastle, and the waves keep changing its shape. In real projects, changes can happen, affecting task times and dependencies. PERT diagrams might need updating.
Dependency on the Critical Path
A chain usually breaks at its weakest link, right? Similarly, if tasks on the critical path aren’t accurate, the whole project’s timing might suffer. It’s crucial to get these right.
Difficulties in Resource Allocation
Assigning resources to tasks in large projects can be complex. You should keep in mind that PERT diagrams don’t always consider these resource constraints.
Constant Monitoring Required
You keep an eye on cooking to avoid burning, right? Similarly, PERT diagrams need regular monitoring. If things change, the diagram might need adjustments.
Collaboration Demands
Did you know that the biggest source of uncertainty comes from a project’s stakeholders? Research shows that about 38% of the time, uncertainty happens because of stakeholders and how they do things. That’s why, while using the PERT method, communication is key to making sure everyone’s on the same page.

From Theory to Reality: Examples of PERT in Project Management
Just like using directions for a road trip, PERT guides projects so they reach their destination smoothly and on time.
1. Designing a New Game
Think about creating a video game. PERT was used to manage designing, coding, and testing. It made sure each step happened at the right time. The good part: the game was finished when planned, and players enjoyed it without any delays.
2. Planting a Garden
Consider planting a garden with different flowers. PERT helped decide when to plant each type, taking into account their growth times. By using PERT, the garden bloomed beautifully, with flowers blooming just when they were supposed to. The result? A well-organized and colorful garden.
Benefits of using the PERT method
- No confusion. First, PERT helped everyone understand what comes next, following a map.
- Avoiding delays: By figuring out which tasks were most important, things stayed on track.
- Using time wisely: Next, PERT made sure time was used well, preventing last-minute rushes.
- Working together: It also helped everyone on the team know their role.
Getting things done: PERT ensured tasks were finished when they should be.
PERT vs. Critical Path Method (CPM): What’s the Difference?
To better understand what PERT means in project management, it’s useful to look at the main difference between PERT and CPM.
PERT charts and CPM charts are two ways of doing projects. PERT is for when things are a bit uncertain, and tasks can take different amounts of time. It uses different guesses for task times and looks at how tasks are connected.
CPM, on the other hand, is for when things are more predictable, and tasks have fixed times. It’s all about finding the quickest way to finish. PERT looks at the whole project puzzle, while CPM watches the clock.
So, use PERT when things are a bit up in the air, and CPM when things are clear, and you want to be super efficient!

When Are PERT Charts the Most Effective?
PERT charts are powerful. But when they team up with project management tools, it’s like they’ve found their perfect backup band.
Take, for example, Teamly. It provides a visual platform for creating and managing PERT charts. As a result, project managers can see which tasks are important, how they depend on each other, and what uncertainties might pop up.
With features for task management, collaboration, and communication, Teamly enables efficient coordination among team members and partners. Additionally, it offers analytical capabilities to identify critical paths and optimize the project schedule.
Plus, integration with other project management features improves the overall project planning and management process.
Overall, project management tools provide the necessary functionalities to maximize the benefits of using PERT charts in project management.
Key Takeaways
PERT isn’t just some fancy acronym. Learning about PERT in project management might just be your golden ticket to more successful project closeout and delivery.
With PERT, you can zoom in on those critical paths. You’ll know which tasks are important and which ones are the wildcards that could throw you off track.
But here’s where it gets really interesting: PERT holds hands with project management tools, creating a power duo that’s hard to beat. When used together, they help you track progress, divvy up resources, and keep your timelines in check.